IEC Reference Designations

The IEC publishes a series of documents and rules governing the preparation of documents, drawings and the referencing of equipment. Depending on country and industry, people are either familiar with the IEC system or not. For those not familiar it can be a little confusing at first.
Often when IEC document production is compared to other methods it is mistakenly assumed the difference is simply symbols. This is not the case. The IEC document and referencing system is a comprehensive approach covering symbols, drawing and layout techniques, equipment references, identification of terminals and signals, classification of documents and computer data organisation. It also goes beyond just documentation and extends into physical devices and implementation.
I've introduced IEC systems to three companies. In each case my initial attempts were meet with criticism, objections and the belief that it was unduly complicating life. However, in all these cases and after a couple of projects everyone on the team was highly praising of the IEC method and were not willing to go back to their old system. In each case implementation of IEC based methods resulting in simplification of documents (drawings), better technical content on the documents, more consistency between documents and a reduction in the time to necessary produce the documents.
One of the areas of the IEC system which is sometimes confuses the first time people come across it is the formulation of reference designations. This note gives a brief overview and introduction to the reference designation system.
Aspects
In defining designations, prefix aspects are used:
| Prefix | Aspect | | = | Function - what does the product do | | - | Product - (how is the object constructed | | + | Location - where is the object located | | The prefix is used to construct single level designations,
which shall consist of the following: - a letter code;
- a letter code followed by a number
-
a number |
The IEC system allows drawing elements and products to be specified in either the functional, product or location aspect or some combination of two or more aspects. Still sounds a little confusing? Hopefully and example will make it easier to understand.
Application by Example
The IEC is fairly open on how you apply reference designations for projects and organisations. Each project or organisation tends to be unique so this makes some sense. For some recent projects we have used to following application of the reference designation system, which works has worked reasonably well . The approach is to ensure that the complete reference designation (tag number) for each item of equipment has a function part and a product part. The location aspect is considered optional and only if required. Some examples:
Function aspect [=]
For the function aspect, we use a variation of the principals set out in IEC 61346-2. For example we use =N for a 400 V supply, if there are two independent feeds we may use =N1 and =N2, etc.
| Code | Definition | Examples |
| H | Installations for 30 kV ... <45 kV | |
| J | Installations for 20 kV ... <30 kV | |
| K | Installations for 10 kV ... <20 kV | |
| L | Installations for 6 kV ... < 10 kV | |
| M | Installations for 1 kV ... < 6 kV | |
| N | Installations < 1 kV | |
| P | Equipotential bonding | Earthing protection
Lightning protection |
| V | Storage of material goods | Fuel Oil |
| X | Auxiliary purpose outside main process | Alarm system, Clock system
Lighting installation
Electric power distribution
Fire protection system
Security system |
| Y | Communication and information tasks | Computer networks
Telephone system
Video surveillance system
Antenna System |
Product Aspect [-]
Product aspect is in accordance with IEC 81346-2, code letters – see later in the note for a more detailed explanation. Typical code letters include Q for circuit breakers, T for transformers, A for assemblies (switchboards), etc. There are specified in more detail in IEC 60617 for each type of device.
Generally we number each product in a logical fashion which fits the project (i.e. -Q1, -Q2, -Q3, etc.). For switchboards (Assemblies) we treat slightly different as shown in the table below. This makes the reference designation more meaningful without over complicating the implementation.
| Code | Description |
| -A0xx | Main Distribution Boards |
| -A1xxx | Sub Main (MCCB) Distribution Boards |
| -A2xxx | Motor Control Centres |
| A3xxx | Local Motor Control Panel |
| -A4xxx | not used |
| -A5xxx | not used |
| -A6xxx | Distribuion Boards (MCB) |
"xxx' represents an optional number.
Initially we did tried to fix 'xxx' across projects to have some useful meaning. This didn't work to well, so basically we allocate the numbers logically depending on the project and arrangement of systems.
Location Aspect [+]
We leave the function aspect is freely definable. Generally we find we do not need to use location as this tends to be obvious from the context of the document or drawings. If we do need to use we would define logical set of locations for the project. These may typically be things like +L23 (level 23), +Z01 (zone 1) etc.
Hierarchy
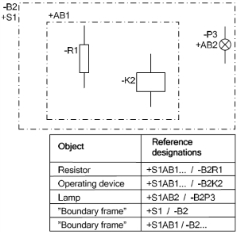 Reference Designation Example
Reference Designation Example IEC structuring is hierarchical in nature. For example if switchboard =N-A1 contains a circuit breaker -Q1 then the full designation of the circuit breaker would be =N1-A1-Q1 (or more simply =N-A1Q1). If the same circuit breaker contains a relay -K12, the full reference would be =N-A1Q1K12. This is further illustrated in the image. This feature of the system makes it easy to number everything uniquely and allows for more commonality in the drawings.
Project Examples
Some more example designations from a current project of ours:
- =J03-Q0, =J03-T1
- =N1-A01, =N1-Q1, =N1-A614
- =N1-A104W614
- =N1-G1
IEC 81346-2 Classification of Objects
IEC 81346-2 "Industrial systems, installations and equipment and industrial products - Structuring principles and reference designations - Part 2: Classification of objects and codes for classes"
IEC 81346-2, published jointly by IEC and ISO defines classes and subclasses of objects based on a purpose- or task-related view of the objects, together with their associated letter codes to be used in reference designations. The classification is applicable for objects in all technical areas, e.g. electrical, mechanical and civil engineering as well as all branches of industry, e.g. energy, chemical industry, building technology, shipbuilding and marine technology, and can be used by all technical disciplines in any design process.
The Letter Codes
A letter codes enables classification of objects. The new letter codes, which are common to all technical branches, apply from IEC 81346-2 table 1.
There are in total 18 classes, identified by the following letter codes:
A - Two or more purposes or tasks
B -Converting an input variable into a signal for further processing
C - Storing of energy, information or material
E - Providing radiant or thermal energy
F - Direct protection from dangerous or unwanted conditions
G -Initiating a flow of energy or material
H -Producing a new kind of material or product
K - Processing signals or information
M - Providing mechanical energy for driving purposes
P - Presenting information
Q - Controlled switching or varying a flow of energy, of signals or of material
R - Restricting or stabilizing motion or a flow of energy, information or material
S - Converting a manual operation into a signal for further processing
T - Conversion of energy maintaining the kind of energy
U - Keeping objects in a defined position
V - Processing (treating) of material or products
W - Guiding or transporting from one place to another
X - Connecting objects
Summary
The above is a very brief introduction to the IEC reference designation system. It is not an easy subject to cover briefly and is better understood by working with the system and seeing live examples. When applied to projects, it does fall into context and everything starts to make sense.
IEC Related Standards
- Designation
- IEC 81346: Structuring principles and reference designations
- IEC 61175: Designation of signals
- IEC 61666: Identification o terminals within a system
- Symbols
- IEC 60617: Graphical symbols for diagrams - maintained as a database
- ISO 81714: Design of graphical symbols
- ISO 14617: Graphical symbols for diagrams
- Documentation Rules
- IEC 61355: Classification and designation for documents
- IEC 62023: Structuring of technical information and documentation
- IEC 82045: Document management
- Preparation of Documents
- IEC 60848: Preparation of sequential function charts
- IEC 61082: Proportion of documents used in electrotechnology - key document for drawings
- IEC 62027: Preparation of part lists
- IEC 62079: Preparation of instructions
- Data Organisation
- IEC 82045: Meta data
- IEC 61360 Data element types
- ISO 10303: Step data model