Lithium Ion Battery
Over recent years the Lithium Ion battery has become popular in applications requiring high power densities with small weight and footprint. Today Lithium Ion batteries are commonly found in mobile phones, portable electronics, power tools, electrically operated vehicles and military applications. In addition to high power densities, Lithium Ion batteries are chargeable and have no memory effect.
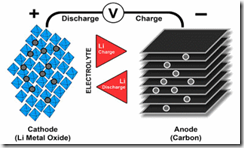
Charge/discharge mechanism of a Lithium Ion battery
Image Source: http://batteryuniversity.com Developed in the early 1970's at Birmingham University in the UK, Lithium Ion batteries consist of a Lithium Metal Oxide positive electrode (cathode), carbon negative electrode (anode) and electrolyte of a lithium salt organic solution. During the discharge process, Lithium Ions move from the negative to the positive electrode, via the external circuit. During the charging the process is reversed by applying an over voltage.
The Lithium Metal Oxide cathode is constructed using various metals with resulting differences in performance:
- Lithium Cobalt Oxide - high energy density, some safety issues
- Lithium Iron Phosphate - low energy density, long life, safe
- Lithium Manganese Oxide - low energy density, long life, safe
- Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide - low energy density, long life, safe
- Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide - special applications
- Lithium Titanate - special applications
Advantages of Lithium Ion Batteries:
- variety of shapes and sizes
- lighter than other battery types
- no memory effect
- low self discharge rate (5-10% per month)
- low maintenance
Disadvantages of Lithium Ion Batteries:
- capacity diminishes with charging
- internal resistance increases with charging
- capacity loss increases at high temperatures
- capacity loss on ageing
As a note of caution, there is the possibility of thermal runaway if a Lithium Ion battery is over charged. Where this is a risk, internal fail safe circuits to shut battery down are incorporated.
Typical Battery Characteristics
| Lithium Cobalt
LiCoO2 | Lithium Manganese
LiMn2O4 | Lithium Iron Phosphate
LiFePO4
| Lithium Manganese Cobalt Oxide
LiNiMnCoO2 | Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide
LiNiCoAlO2 | Lithium Titanate
Li4Ti5O12
|
| | LCO | LMO | LFP | NMC | NCA | LTO |
| Voltage | 3.60V | 3.80V | 3.30V | 3.60/3.70V | | 2.4V |
| Charge Limit | 4.20V | 4.20V | 3.60V | 4.20V | | |
| Cycle Life | 500–1,000 | 500–1,000 | 1,000–2,000 | 1,000–2,000 | | |
| Operating Temperature | Average | Average | Good | Good | | |
| Specific Energy | 150–190Wh/kg | 100–135Wh/kg | 90–120Wh/kg | 140-180Wh/kg | | |
| Safety | Average. Needs protection circuit.
| Average. Needs protection circuit.
| Very safe. Needs voltage protection. | Safe. Needs protection circuit. | | |
| Thermal. Runaway | 150°C
(302°F) | 250°C
(482°F) | 270°C
(518°F) | 210°C
(410°F) | | |
| In Use Since | 1994 | 1996 | 1999 | 2003 | | |
| Application | very high specific energy, limited power; cell phones, laptops | high power, good to high specific energy; power tools, medical | high power, average
specific energy, elevated self-discharge | very high specific energy, high power; tools, medical
| electric powertrain and grid storage
| electric powertrain and grid storage |
Storage
Capacity loss due to storage is a problem with Lithium Ion batteries. This loss is dependent on the charge state, storage time and storage temperature. The normal recommendation is to store batteries approximately 40% charged. If stored for one year at 40% charge and 0oC, the recoverable capacity at the end of this period would be around 98%. As storage temperature increases to 60oC, the recoverable charge will decrease typically to around 75%. If the batteries were fully charged the recoverable charge would be 94% and 60%.
If anyone has any tips or other information to add, just leave a comment and I’ll incorporate it into the article.