Understanding Motor Duty Rating
One of the comments on my Motor Starting Series was asking for something on duty cycles. Here it is.
As a purchaser of a motor, you have responsibility to let the manufacturer know the anticipated duty of the motor. To assist in the communication of this information, the standard IEC 60034-1 (Rotating electrical machines) defines several duty characteristics, denoted S1 to S10:
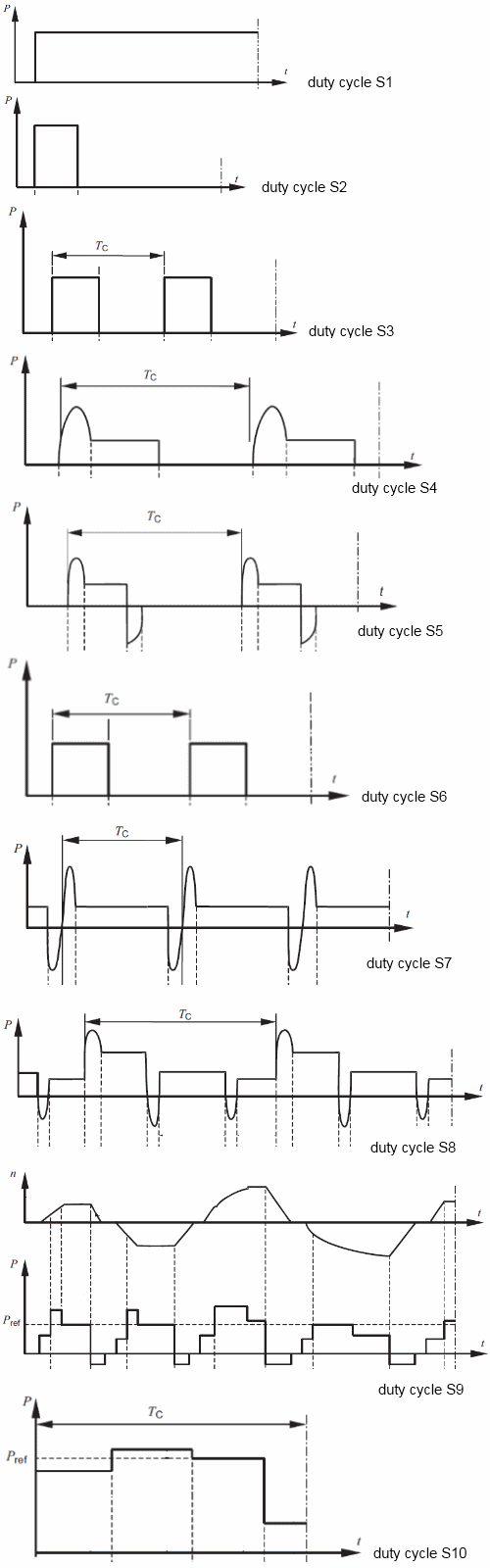
| S1 |
Continuous duty |
The motor operates at a continuous load for sufficient time to enable machine to reach thermal equilibrium. |
| S2 |
Short Time duty |
Operation at a load for a time not sufficient to reach thermal equilibrium, followed by enough time for the motor to cool down. |
| S3 |
Intermittent periodic duty
|
Series of identical duty cycles each a constant load for a period, followed by a rest period. Thermal equilibrium is not reached during the cycle. |
| S4 |
Intermittent periodic duty with starting |
Similar to S3, but there is a significant starting time within the periodic operation. |
| S5 |
Intermittent periodic duty with electric braking |
Sequence of identical duty cycles - starting, operation, braking and rest. Again thermal equilibrium is not reached. |
| S6 |
Continuous operation periodic duty |
Identical duty cycles with a period at load followed by a period at no load. Difference between S1 is that the motor runs at no-load, without actual stopping. |
| S7 |
Continuous operation periodic duty with electric braking |
As per S6, but with a significant starting and electric breaking periods. Again motor operates at no-load for period instead of stopped. |
| S8 |
Continuous operation periodic duty with related load/speed changes |
Series of identical repeating duty cycles, where within each cycle the motor operates at several different load levels and speed. There is not stopped time and thermal equilibrium is not reached. |
| S9 |
Duty with non-periodic load and speed variations |
Load and speed vary periodically within the permissible operating range. Frequent overloading may occur. |
| S10 |
Duty with discrete constant loads and speeds |
Duty with discrete number of load/speed combinations, with these maintained long enough to reach thermal equilibrium. |
Thermal Equilibrium is the state reached when the temperature rise of the machine does not vary by more than 2K per hour. If you don't specify the duty cycle, the manufacturer will likely assume S1. Click on the image to see a larger version, illustrating the duty cycles.
If anyone has anything to add, please do so below.