Motor Efficiency Classification
Electric motors are one of the most widely used items of electrical equipment. Improving motor efficiency benefits include, reduced power demand, lower operating costs and reduced environment impact.
In recognising the impact of motors on both power generation requirements and environmental issues, regulation in many countries now dictate efficiency limits. When specifying motors, both designers and purchasers should be concerned with efficiency performance.
Within the note, we look at both the European Efficiency Classification and IEC 60034 Efficiency Limits. At the end we give some guidance on how to calculate the cost savings associated with the user of higher efficiency motors.
European Efficiency Classification
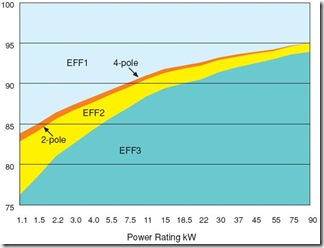
European Efficiency Classification The European Scheme to designate energy efficiency classes for low voltage AC motors has been in operation since 1999. The scheme established through co-opera ton between CEMEP and the European Commission is an important element of the European efforts to improve energy efficiency and thus reduce CO2 emissions.
How it works
Motors are defined by levels of efficiency per kW rating and the number of poles. The efficiency is expressed at both full load and 3/4 load and labels must appear on the motor.
Motors included in the scheme are defined as totally enclosed fan ventilated (normally IP 54 or IP 55), three phase AC, squirrel cage [[induction motor|induction motors]] in the range of 1.1 to 90 kW, rated for 400 V, 50 Hz, S1 duty class standard design.
Efficiency values
For motors designed 380 to 400 V with efficiency values based on 400 V.
| 2 pole motor specified efficiencies (%) |
| kW |
EFF1 |
EFF2 |
EFF3 |
| 1.1 |
>= 82.8 |
>= 76.2 |
< 76.2 |
| 1.5 |
>= 84.1 |
>= 78.5 |
< 78.5 |
| 2.2 |
>= 85.6 |
>= 81 |
< 81 |
| 3 |
>= 86.7 |
>= 82.6 |
< 82.6 |
| 4 |
>= 87.6 |
>= 84.2 |
< 84.2 |
| 5.5 |
>= 88.6 |
>= 85.7 |
< 85.7 |
| 7.5 |
>= 89.5 |
>= 87 |
< 87 |
| 11 |
>= 90.5 |
>= 88.4 |
< 88.4 |
| 15 |
>= 91.3 |
>= 89.4 |
< 89.4 |
| 18.5 |
>= 91.8 |
>= 90 |
< 90 |
| 22 |
>= 92.2 |
>= 90.5 |
< 90.5 |
| 30 |
>= 92.9 |
>= 91.4 |
< 91.4 |
| 37 |
>= 93.3 |
>= 92 |
< 92 |
| 45 |
>= 93.7 |
>= 92.5 |
< 92.5 |
| 55 |
>= 94 |
>= 93 |
< 93 |
| 75 |
>= 94.6 |
>= 93.6 |
< 93.6 |
| 90 |
>= 95 |
>= 93.9 |
< 93.9 |
|
| 4 pole motor specified efficiencies (%) |
| kW |
EFF1 |
EFF2 |
EFF3 |
| >= 1.1 |
83.8 |
>= 76.2 |
< 76.2 |
| >= 1.5 |
85 |
>= 78.5 |
< 78.5 |
| >= 2.2 |
86.4 |
>= 81 |
< 81 |
| >= 3 |
87.4 |
>= 82.6 |
< 82.6 |
| >= 4 |
88.3 |
>= 84.2 |
< 84.2 |
| >= 5.5 |
89.2 |
>= 85.7 |
< 85.7 |
| >= 7.5 |
90.1 |
>= 87 |
< 87 |
| >= 11 |
91 |
>= 88.4 |
<8 8.4 |
| >= 15 |
91.8 |
>= 89.4 |
< 89.4 |
| >= 18.5 |
92.2 |
>= 90 |
< 90 |
| >= 22 |
92.6 |
>= 90.5 |
< 90.5 |
| >= 30 |
93.2 |
>= 91.4 |
< 91.4 |
| >= 37 |
93.6 |
>= 92 |
< 92 |
| >= 45 |
93.9 |
>= 92.5 |
< 92.5 |
| >= 55 |
94.2 |
>= 93 |
< 93 |
| >= 75 |
94.7 |
>= 93.6 |
< 93.6 |
| >= 90 |
95 |
>=9 3.9 |
< 93.9 |
|
IEC 60034 Efficiency Limits
_thumb.png)
IEC 60034 Efficiency Limits IEC 60034-30 defines three efficiency classes for of single speed, three phase, cage induction motors.
IE1 - Standard efficiency (efficiency levels roughly equivalent to EFF2)
IE2 - High efficiency (efficiency levels roughly equivalent to EFF1, identical to EPAct in USA)
IE3 - Premium efficiency (identical to "NEMA
Premium" in the USA)
IEC 60034-30 covers almost all motors, with the notable exceptions of motors made solely for converter operation and motors completely integrated into a machine (and which cannot be tested separately) .
IEC 60034 Efficiency Limits
Efficiency limit values IEC 60034-30; 2008
Output
kw |
IE1 - Standard Efficiency |
IE2 - High Efficiency |
IE3 - Premium Efficiency |
| 2 pole |
4 pole |
6 pole |
2 pole |
4 pole |
6 pole |
2 pole |
4 pole |
6 pole |
| 0.75 |
72.1 |
72.1 |
70.0 |
77.4 |
79.6 |
75.9 |
80.7 |
82.5 |
78.9 |
| 1.1 |
75.0 |
75.0 |
72.9 |
79.6 |
81.4 |
78.1 |
82.7 |
84.1 |
81.0 |
| 1.5 |
77.2 |
77.2 |
75.2 |
81.3 |
82.8 |
79.8 |
84.2 |
85.3 |
82.5 |
| 2.2 |
79.7 |
79.7 |
77.7 |
83.2 |
84.3 |
81.8 |
85.9 |
86.7 |
84.3 |
| 3 |
81.5 |
81.5 |
79.7 |
84.6 |
85.5 |
83.3 |
87.1 |
87.7 |
85.6 |
| 4 |
83.1 |
83.1 |
81.4 |
85.8 |
86.6 |
84.6 |
88.1 |
88.6 |
86.8 |
| 5.5 |
84.7 |
84.7 |
83.1 |
87.0 |
87.7 |
86.0 |
89.2 |
89.6 |
88.0 |
| 7.5 |
86.0 |
86.0 |
84.7 |
88.1 |
88.7 |
87.2 |
90.1 |
90.4 |
89.1 |
| 11 |
87.6 |
87.6 |
86.4 |
89.4 |
89.8 |
88.7 |
91.2 |
91.4 |
90.3 |
| 15 |
88.7 |
88.7 |
87.7 |
90.3 |
90.6 |
89.7 |
91.9 |
92.1 |
91.2 |
| 18.5 |
89.3 |
89.3 |
88.6 |
90.9 |
91.2 |
90.4 |
92.4 |
92.6 |
91.7 |
| 22 |
89.9 |
89.9 |
89.2 |
91.3 |
91.6 |
90.9 |
92.7 |
93.0 |
92.2 |
| 30 |
90.7 |
90.7 |
90.2 |
92.0 |
92.3 |
91.7 |
93.3 |
93.6 |
92.9 |
| 37 |
91.2 |
91.2 |
90.8 |
92.5 |
92.7 |
92.2 |
93.7 |
93.9 |
93.3 |
| 45 |
91.7 |
91.7 |
91.4 |
92.9 |
93.1 |
92.7 |
94.0 |
94.2 |
93.7 |
| 55 |
92.1 |
92.1 |
91.9 |
93.2 |
93.5 |
93.1 |
94.3 |
94.6 |
94.1 |
| 75 |
92.7 |
92.7 |
92.6 |
93.8 |
94.0 |
93.7 |
94.7 |
95.0 |
94.6 |
| 90 |
93.0 |
93.0 |
92.9 |
94.1 |
94.2 |
94.0 |
95.0 |
95.2 |
94.9 |
| 110 |
93.3 |
93.3 |
93.3 |
94.3 |
94.5 |
94.3 |
95.2 |
95.4 |
95.1 |
| 132 |
93.5 |
93.5 |
93.5 |
94.6 |
94.7 |
94.6 |
95.4 |
95.6 |
95.4 |
| 160 |
93.7 |
93.8 |
93.8 |
94.8 |
94.9 |
94.8 |
95.6 |
95.8 |
95.6 |
| 200 |
94.0 |
94.0 |
94.0 |
95.0 |
95.1 |
95.0 |
95.8 |
96.0 |
95.8 |
| 250 |
94.0 |
94.0 |
94.0 |
95.0 |
95.1 |
95.0 |
95.8 |
96.0 |
95.8 |
| 315 |
94.0 |
94.0 |
94.0 |
95.0 |
95.1 |
95.0 |
95.8 |
96.0 |
95.8 |
| 355 |
94.0 |
94.0 |
94.0 |
95.0 |
95.1 |
95.0 |
95.8 |
96.0 |
95.8 |
| 375 |
94.0 |
94.0 |
94.0 |
95.0 |
95.1 |
95.0 |
95.8 |
96.0 |
95.8 |
From June 16, 2011 machine builders are only permitted to use high-efficiency motors with a minimum efficiency class of IE2 (IEC 60034:2008). The new EU Directive 2005/32/EC is applicable to low-voltage asynchronous motors of 0.75 to 375 kW.
The aim of the change is that by reducing losses, carbon-dioxide emissions and operating costs are reduced.
Calculation of cost savings
A quick calculation of annual savings is given by:
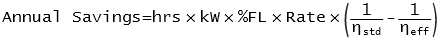
where:
- hrs = annual running time (hours)
- kW = motor rating in kW
- %FL = fraction of full load power motor is running at
- Rate = electricity cost per kWh
- ηstd = efficiency of standard motor
- ηeff = efficiency of better motor