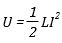Inductance
When current flows within a wire, a magnetic field is created. The potion of this magnetic field perpendicular to the wire is called the magnetic flux (measured in weber, Wb). Inductance is the ratio of magnetic flux to current in a circuit. The unit of inductance is the henry, H (Wb/A) and is normally represented by the symbol L.
Self Inductance
Whenever current in a coil of wire changes, the magnetic field]it produces will change. That will change the magnetic flux through the coil and hence produce a voltage across the coil. This is called self-inductance, and the coil is referred to as an inductor.
Example – Self Inductance of a Solenoid
Consider a coil of wire around a magnetic core, whose length is much greater than it's diameter.
Given the permeability of free space μo , relative permeability of the magnetic core μr , number of turns N and length of solenoid l, with a current i flowing, the magnetic flux density, B within the coil is is given by:
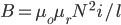
The magnetic flux, Φ is obtained by multiplying flux density by the cross sectional area A:
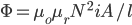
Given that the inductance is the ratio of magnetic flux to current, we have:
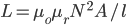
Note: if the solenoid is wound around a non-magnetic core, then μr = 1.
Mutual Inductance
When the magnetic field of one coil links with that of another coil, a change in current in the first coil will produce a linking magnetic field with the second coil. The magnetic field linking with the second coil will produce a voltage within that coil. This is called mutual inductance.
For two inductors (coils) we have:
- L11 – self inductance of inductor 1
- L22 – self inductance of inductor 2
- L12 = L21 – mutual inductance between the two
Inductance Formulae
The table below lists some common formulae for calculating the theoretical inductance of several inductor constructions.
- L = inductance (H)
- μ0 = permeability of free space = 4 π× 10-7 (H/m)
- μr = relative permeability of core material
Cylindrical coil:
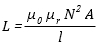 |
N = number of turns
A = area of cross-section of the coil in square metres (m2)
l = length of coil in metres (m) |
Straight wire conductor:
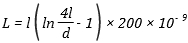 |
l = length of conductor (m)
d = diameter of conductor (m) |
Flat spiral air-core coil:
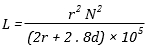 |
r = mean radius of coil (m)
N = number of turns
d = depth of coil (outer radius minus inner radius) (m) |
Toroidal core, circular cross-section:
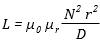 |
N = number of turns
r = radius of coil winding (m)
D = overall diameter of toroid (m) |
Application to Circuits
The quantitative measure of applying an inductance L, to a circuit defined by:
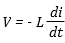
An inductor can store energy. The power (= energy / time) being stored in an inductor is:
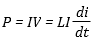
This implies (by a little calculus) that the energy stored in an inductor is :