What is an Open Delta Transformer
In three phase systems, the use of transformers with three windings (or legs) per side is common. These three windings are often connected in delta or star, resulting in common transformer configurations such as delta-delta or delta-star. An open delta transformer is a special arrangement which uses only two windings.
If your new to transformers, have a look at the Power Transformers - An Introduction note.
Transformer Configuration
The illustration shows how an open delta transformer is connected. On both the primary and secondary there are only two windings. Even in this configuration, it is still possible to transform a three phase voltage.
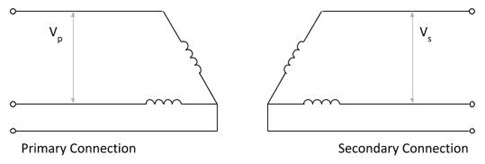 Open Delta Transformer
Open Delta Transformer Open delta transforms are not the commonly used. Typically they would be used for small loads where cost is important. Alternatively, they could be used as an emergency measure, should one winding only of a transformer fail.
Sometimes you may hear an open delta transformer referred to as a V-connection transformer.
Power Delivered
Sometimes the power delivered by an open delta transformer is compared to that of an equivalent three winding transformer. Typically figures like having 57.7% of the capacity of an equivalent three winding transformer or 87% of two transformers (same winding size) are quoted. While you can think of the transformer in this manner, it is more fruitful not to consider comparisons but to the necessary calculations on the open delta transformer.
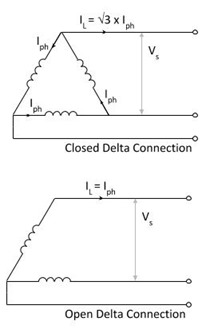
Consider the illustration, showing the output from both a close delta and open delta transformer. Note, that in the delta connection to line current is √3 times the phase current, whereas in the open delta, they are the same.
The transformer output power (in VA) is for a balanced transformer system for the closed delta connection (using phase current), this give:
And for the open delta connection:
Taking the ratio of open delta to closed delta power, gives:
Summary
Open delta transformers are three phase devices, with only two windings on each of the primary and secondary sides. While cheaper than a conventional three winding transformer, the open delta will only deliver 57.7% of the power of a conventional transformer (not two thirds, 66.7% as may be expected). There is limited adoption of open delta transformers, although they can be useful in certain situations.