Cost Performance and Time
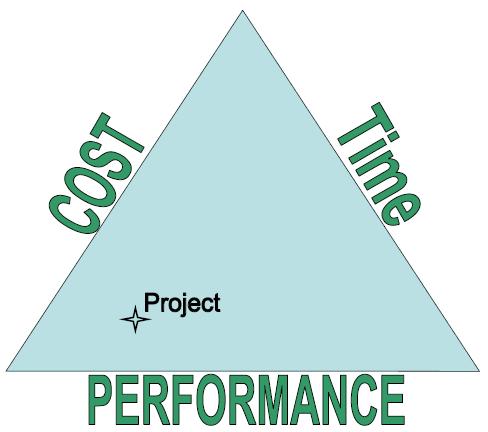 |
Cost and Performance in this project
are more important than time |
Often us engineers get so bogged down in equations, using software, producing drawings and writing specifications that this becomes the sole focus. Good engineering design needs to go beyond the technical and look at the full picture. A good way to measure this is cost, performance and time.
Cost is an important aspect of any project, yet often only considered at a cursory level. If two designs perform the same, but one costs less than it could be argued that the cheaper design is the better design. Good engineering should always strive for cost effectiveness.
Performance is the second measure. Performance means ensuring the technical and specification requirements of the project are realised. If something does not perform as expected (or worse not at all), then the engineering has not been up to scratch. Luckily concentrating on performance is the natural habitat for most of us.
Time is the final measure. All projects take time to design and things need to happen within a reasonable time frame. While some projects are more time sensitive than other, all projects will (should) have some form of time constraint.
Putting it all together
Each project is different and the easiest way to visualise this is the engineering triangle (see illustration). The requirements for any particular project are located within the triangle, the position being indicative of the relative importance of the cost, performance and time. Some projects will be more performance centric (a NASA space probe for example). Others would be more cost centric (a lens for a disposable camera) or time critical (projects where a completion date has been publicly announced).
Knowing how cost, performance and time interrelate on a project should guide the engineering design. The end result of considering these project measures is always a better engineered design.