ANSI (IEEE) Protective Device Numbering
The widely used United Sates standard ANSI/IEEE C37.2 'Electrical Power System Device Function Numbers, Acronyms, and Contact Designations' deals with protective device function numbering and acronyms. Even in those parts of the world where IEC standards are predominate, the use of ANSI numbering for protective device functions is still common place.
Protective Device Numbers
Protective relays are commonly referred to by standard device numbers. For example, a time overcurrent relay is designated a 51 device, while an instantaneous overcurrent is a 50 device. Multifunction relays have combinations of device numbers. A 27/59 device, for example, is a combination under/over voltage relay. Letters can be added to clarify application (87T for transformer differential, 59G for ground overvoltage).
- 1 – Master Element
- 2 – Time Delay Starting or Closing Relay
- 3 – Checking or Interlocking Relay
- 4 – Master Contactor
- 5 – Stopping Device
- 6 – Starting Circuit Breaker
- 7 – Rate of Change Relay
- 8 – Control Power Disconnecting Device
- 9 – Reversing Device
- 10 – Unit Sequence Switch
- 11 – Multi-function Device
- 12 – Overspeed Device
- 13 – Synchronous-speed Device
- 14 – Underspeed Device
- 15 – Speed – or Frequency, Matching Device
- 16 – Data Communications Device
- 17 – Shunting or Discharge Switch
- 18 – Accelerating or Decelerating Device
- 19 – Starting to Running Transition Contactor
- 20 – Electrically Operated Valve
- 21 – Distance Relay
- 22 – Equalizer Circuit Breaker
- 23 – Temperature Control Device
- 24 – Volts Per Hertz Relay
- 25 – Synchronizing or Synchronism-Check Device
- 26 – Apparatus Thermal Device
- 27 – Undervoltage Relay
- 28 – Flame detector
- 29 – Isolating Contactor or Switch
- 30 – Annunciator Relay
- 31 – Separate Excitation Device
- 32 – Directional Power Relay
- 33 – Position Switch
- 34 – Master Sequence Device
- 35 – Brush-Operating or Slip-Ring Short-Circuiting Device
- 36 – Polarity or Polarizing Voltage Devices
- 37 – Undercurrent or Underpower Relay
- 38 – Bearing Protective Device
- 39 – Mechanical Condition Monitor
- 40 – Field (over/under excitation) Relay
- 41 – Field Circuit Breaker
- 42 – Running Circuit Breaker
- 43 – Manual Transfer or Selector Device
- 44 – Unit Sequence Starting Relay
- 45 – Abnormal Atmospheric Condition Monitor
- 46 – Reverse-phase or Phase-Balance Current Relay
- 47 – Phase-Sequence or Phase-Balance Voltage Relay
- 48 – Incomplete Sequence Relay
- 49 – Machine or Transformer, Thermal Relay
- 50 – Instantaneous Overcurrent Relay
- 51 – AC Inverse Time Overcurrent Relay
- 52 – AC Circuit Breaker
- 53 – Exciter or DC Generator Relay
- 54 – Turning Gear Engaging Device
- 55 – Power Factor Relay
- 56 – Field Application Relay
- 57 – Short-Circuiting or Grounding Device
- 58 – Rectification Failure Relay
- 59 – Overvoltage Relay
- 60 – Voltage or Current Balance Relay
- 61 – Density Switch or Sensor
- 62 – Time-Delay Stopping or Opening Relay
- 63 – Pressure Switch
- 64 – Ground Detector Relay
- 65 – Governor
- 66 – Notching or Jogging Device
- 67 – AC Directional Overcurrent Relay
- 68 – Blocking or "Out-of-Step" Relay
- 69 – Permissive Control Device
- 70 – Rheostat
- 71 – Liquid Level Switch
- 72 – DC Circuit Breaker
- 73 – Load-Resistor Contactor
- 74 – Alarm Relay
- 75 – Position Changing Mechanism
- 76 – DC Overcurrent Relay
- 77 – Telemetering Device
- 78 – Phase-Angle Measuring Relay
- 79 – AC Reclosing Relay
- 80 – Flow Switch
- 81 – Frequency Relay
- 82 – DC Reclosing Relay
- 83 – Automatic Selective Control or Transfer Relay
- 84 – Operating Mechanism
- 85 – Communications,Carrier or Pilot-Wire Relay
- 86 – Lockout Relay
- 87 – Differential Protective Relay
- 88 – Auxiliary Motor or Motor Generator
- 89 – Line Switch
- 90 – Regulating Device
- 91 – Voltage Directional Relay
- 92 – Voltage and Power Directional Relay
- 93 – Field Changing Contactor
- 94 – Tripping or Trip-Free Relay
- 95 to 99 – For specific applications where other numbers are not suitable
* for a full definition of each function, please refer to the ANSI/IEEE C37.2 standard
Prefixes and Suffixes
Letters and numbers may be used as prefixes or suffixes to device function numbers to provide a more specific definition of the function. Prefixes and suffixes should, however, be used only when they accomplish a useful purpose.
| Auxiliary devices - C - Closing relay/contactor
- CL - Auxiliary relay, closed
- CS - Control switch
- D - "Down" position switch relay
- L- Lowering relay
- O - Opening relay/contactor
- OP - Auxiliary relay, open
- PB - Push button
- R - Raising relay
- U - "UP" position switch relay
- X - Auxiliary relay
- Y - Auxiliary relay
- Z - Auxiliary relay
Actuating quantities - A -Air/amperes/alternating
- C - Current
- D - Direct/discharge
- E - Electrolyte
- F - Frequency/flow/fault
- GP - Gas pressure
- H - Explosive/harmonics
- I0 - Zero sequence current
- I-, I2 - Negative sequence current
- I+, I1 - Positive sequence current
- J - Differential
- L - Level/liquid
- P - Power/pressure
- PF - Power factor
- Q - Oil
- S - Speed/suction/smoke
- T - Temperature
- V - Voltage/volts/vacuum
- VAR -Reactive power
- VB - Vibration
- W - ater/watts
Other suffix letters - A - Accelerating, automatic
- B - Blocking, backup
- BF - Breaker failure
- C - Close, cold
- D - Decelerating, detonate, down, disengaged
- E - Emergency, engaged
- F - Failure, forward
- GP - General purpose
- H - Hot, high
- HIZ - High impedance fault
- HR - Hand reset
- HS - High speed
- L - Left, local, low, lower, leading
- M - Manual
- O - Open, over
- OFF - Off
- ON - On
- P - Polarizing
- R - Right, raise, reclosing, receiving, remote, reverse
- S - Sending, swing
- SHS - Semi-high speed
- T - Test, trip, trailing
- TDC - Time-delay closing contact
- TDDO - Time delayed relay coil drop-out
- TDO - Time-delay opening contact
- TDPU - Time delayed relay coil pickup
- THD - Total harmonic distortion
- U - Up, under
| Main device - A - Alarm/auxiliary power
- AC - Alternating current
- AN - Anode
- B - Battery, blower, bus
- BK - Brake
- BL - Block (valve)
- BP - Bypass
- BT - Bus tie
- C - Capacitor, condenser, compensator, carrier current, case, compressor
- CA - Cathode
- CH - Check (valve)
- D - Discharge (valve)
- DC - Direct current
- E - Exciter
- F - Feeder, field, filament, filter, fan
- G - Generator/ground
- H - Heater/housing
- L - Line, logic
- M - Motor, metering
- MOC - Mechanism operated contact
- N - Network, neutral
- P - Pump, phase comparison
- R - Reactor, rectifier, room
- S - Synchronizing, secondary, strainer, sump ,suction (valve)
- T -Transformer, thyratron
- TH - Transformer (high-voltage side)
- TL - Transformer (low-voltage side)
- TM - Telemeter
- TOC - Truck-operated contacts
- TT - Transformer (tertiary-voltage side)
- U - Unit
Main device parts - BK - Brake
- C - Coil, condenser, capacitor
- CC - Closing coil, closing contactor
- HC - Holding coil
- M - Operating motor
- MF - Fly-ball motor
- ML - Load-limit motor
- MS - Speed adjusting or synchronizing motor
- OC - Opening contactor
- S - Solenoid
- SI - Seal-in
- T - Target
- TC Trip coil
- V - Valve
Reference positions of devices - Adjusting means - Low or down position
- Clutch - Disengaged position
- Contactor - De-energized position
- Contactor (latched-in type) - Main contacts open
- Density switch - Standard reference
- Disconnecting switch - Main contacts open
- Flow detector - Lowest flow
- Gate - Closed position
- Level detector - Lowest level
- Load-break switch - Main contacts open
- Power circuit breaker - Main contacts open
- Power electrodes - Maximum gap position
- Pressure switch - Lowest pressure
- Reclosure - Main contactor open
- Relay - De-energized position
- Relay (latched-in type)
- Rheostat - Maximum resistance position
- Speed switch - Lowest speed
- Tap changer - Center tap
- Temperature relay - Lowest temperature
- Turning gear - Disengaged position
- Vacuum switch - Lowest pressure that is highest vacuum
- Valve - Closed position
- Vibration detector - Minimum vibration
|
ANSI IEC Comparison
| ANSI | IEC 60617 | Description |
| 21FL | FLOC | Fault locator |
| 21G | Z< | Underimpedance |
| 24 | U/f> | Overexcitation |
| 25 | SYNC | Synchronisation check |
| 27 | U< | Undervoltage |
| 32 | P→ | Directional power relay
32P, P→, - active power
32Q, Q→ - reactive powerpower |
| 37 | I< | Non-directional undercurrent |
| 40 | X< | Underexcitation |
| 46 | I2> | Negative-phase sequence |
| 47 | U2> | Phase-sequence voltage protection |
| 48, 14, 66 | Is²t,n< | Start-up supervision for motors |
| 49F | Ith> | Thermal protection for cables |
| 49M/49G/49T | 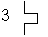 | Three-phase thermal protection for machines
M - motor, G - generators, T - transformer |
| 50N/51N | I0> | Non-directional earth-fault |
| 51 | I> | Non-directional overcurrent
51C, I> - shunt capacitors
51V, I(U)> - voltage dependant |
| 59 | U> | Overvoltage
59N, U0> - residual overvoltage |
| 67 | I>→ | Directional overcurrent
67N, I0>→ - directional earth-fault |
| 68 | I2> | Transformer/motor inrush current |
| 79 | 0→1 | Auto-reclosure |
| 81 | f | Frequency relay
81N, f< - underfrquency
81O, f> - overfrequency |
| 87 | ΔI> | Differential protection
87G, ΔI> - generator
87M, ΔI> - motor
87T, ΔI> - transformer
87N, ΔI0> - restricted earth fault |
Notes:
1. for high set and instantaneous tripping, '>' can be replaced with '>>' or '>>'
2. '3' can be placed before designations to indicate three phase, i.e. 3I<