Three Phase Power Simplified
A single phase system is perhaps the most common type of system most people are familiar with. This is what people have in their homes and what appliances are plugged in to. For larger amounts of power, three phase systems are used.
Electricity is generated by a coil of wire moving through a magnetic field. The illustration shows three such coils in an electrical generator , spaced evenly apart. Each coil is called a phase and as there are three coils, this is called a three phase system.
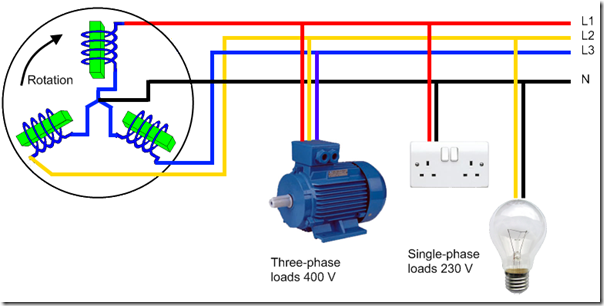
From a such a system, power can be supplied as single phase (load connected between a line and neutral) or three phase (load connected between all three lines). In the illustration, the motor is connected as a three phase load and the socket outlets and lamp as single phase loads.
Terminology
The three winding end connected together at the centre are is called the neutral (denoted as 'N'). The other ends are called the line end (denoted as 'L1', 'L2' and 'L3').
The voltage between two lines (for example 'L1' and 'L2') is called the line to line (or phase to phase) voltage. The voltage across each winding (for example between 'L1' and 'N' is called the line to neutral (or phase voltage).
Voltage Relationship
The line to line voltage is the vector sum of the phase to phase voltage across each winding. This is not the same as the arithmetic sum and is given by the following equation:
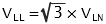 | | Example: Line to Line Voltage (VLL) 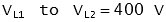 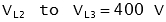
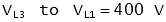
Line to Neutral Voltage (VLN) 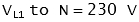
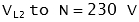
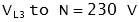
|
Solving Three Phase Problems
Tip - to solve a three phase problem, convert it to a single phase problem.
In a balanced three phase system
- each phase delivers/uses 1/3 of the total power
- convert three phase problems to single phase
Resources