Operational Amplifier
The fundamental component of any analogue computer is the operational amplifier, or op amp. An operational amplifier (often called an op-amp,) is a high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output.
Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices. Many standard IC op-amps cost only a few cents in moderate production volume; however some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost significantly more.
Operation
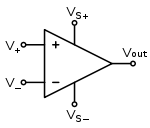 The amplifier's differential inputs consist of a V+ input and a V input, and ideally the op amp amplifies only the difference in [[voltage]] between the two (called the differential input voltage). The output voltage of the op-amp is given by the equation:
The amplifier's differential inputs consist of a V+ input and a V input, and ideally the op amp amplifies only the difference in [[voltage]] between the two (called the differential input voltage). The output voltage of the op-amp is given by the equation:
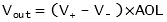
where V+ is the voltage at the non-inverting terminal, V- is the voltage at the inverting terminal and AOL is the open-loop gain of the amplifier.
The magnitude of AOL is typically very large (seldom less than a million) and even a quite small differential input voltage will result in amplifier saturation.
If linear operation is desired, negative feedback must be used and is usually achieved by applying a portion of the output voltage to the inverting input. The feedback enables the output of the amplifier to keep the inputs at or near the same voltage so that saturation does not occur.
Idea Op Amp
An ideal op-amp is would have the following properties. In practice, none of these ideals can be realized, and various shortcomings and compromises have to be accepted.
- Infinite open-loop gain
- Infinite voltage range available at the output
- Infinite bandwidth
- Infinite input impedance
- Zero input current
- Zero input offset voltage
- Infinite slew rate
- Zero output impedance
- Zero noise
- Infinite common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR)
- Infinite power supply rejection ratio
Applications
Op-amps are often used in electronic circuit design. The use of op-amps as circuit blocks is generally much easier and clearer than specifying all their individual circuit elements ([[transistors]],[[resistor| resistors]], etc.).
Basic Op 'Amp' Circuits
Voltage Gain of Op-amps
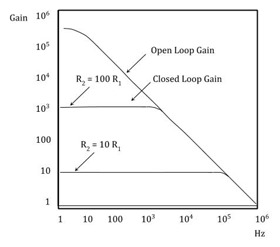 Op-amp Gain
Op-amp Gain Real op-amp such as the commonly available uA741, do not have infinite gain or bandwidth but have a typical "Open Loop Gain". This is defined as the amplifiers output amplification without any external feedback signals connected to it and for a typical operational amplifier is 105 to 106 at DC (zero Hz). This output gain decreases linearly with frequency down to "Unity Gain" or 1, at about 1MHz.