Thermoplastic and Thermosetting Insulation
 While there are a vast array of cable insulation materials, these are often divided into two general types; Thermoplastic or Thermosetting. For example the current capacity determination of a cable in accordance with the UK Wiring Regulations is categorized into thermoplastic and thermosetting cables.
While there are a vast array of cable insulation materials, these are often divided into two general types; Thermoplastic or Thermosetting. For example the current capacity determination of a cable in accordance with the UK Wiring Regulations is categorized into thermoplastic and thermosetting cables.
Thermoplastic materials are composed of chains of molecules (polyethylene for example). When heat is applied the energy will allow the bonds to separate and the material can flow (melt) and be reformed.
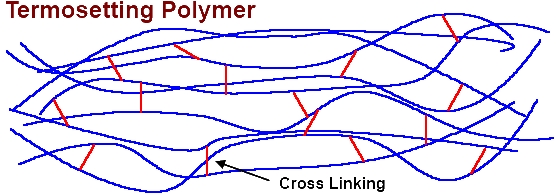
Thermosetting materials are formed when materials such as polyethylene undergo specific heating or chemical processes. During this process the individual chains become cross linked by smaller molecules making a rigid structure. Thermosetting materials cannot reheated, melted and remolded.
While thermoplastic materials have the advantage of being able to be reformed, thermosetting materials are generally more heat resistance and have greater strength.
The operating temperature of any cable is an important parameter in determining the maximum allowable current. While the actual temperature varies depending on the material used, the UK Wiring Regulations limits the choice in calculating the current rating to two temperatures only:
Note: more specific calculations based on actual material properties are allowed. However, for ease of use most practical application will use 70 oC or 90 oC and the methods outlined in the regulations.
See Also