Harmonised Cable Codes and Colours
Within Europe the European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) has standardised the both the designation and colour of cables. These are published in CENELEC document HD 361 S3:1999 "System for cable designation" and HD 308 S2: 2001
"Identification of cores in cables and flexible cords". This note provides a general overview to the harmonised system and gives some examples.
Cable Designation
The HD 261 document, classifies the construction of the cable by allocating codes (letters or numbers) to represent the cable voltage, insulation material\, structural elements, sheath, special features and conductor type.
For a full list of codes and their meanings, it is best to refer to the standard. A typical cable specification would take the form of:
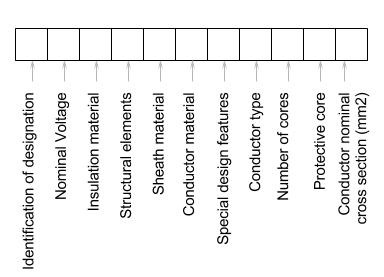
Laying out the Harmonised Cable Code
The layout of the cable code can be split into three parts. Fist the standard and nominal voltage are given. This is followed by the insulation material, construction features and sheath. Finally the cores and cross section are specified.
Each cable element is designated with a alpha numeric code as detailed in the tables below. Typically these are connected together to form the final cable designation. Optional codes or codes that have no relevance to the cable under consideration are simply omitted.
Note: some codes are preceded by a '-' sign, for example -A (aluminium).
Designation Codes
| Identification of Designation
A authorised national standard
H harmonised standard
Nominal Voltage
01 100 V
03 300/300 V
05 300/500 V
07 450/750 V
Structural Elements
- Concentric Conductors
A Concentric aluminium conductor
A6 Concentric aluminium conductor, meander-shaped
C Concentric copper-conductor
C6 Concentric copper-conductor, meander-shaped
C9 Divided concentric copper conductor
- Screen
A7 Aluminium screen
A8 Aluminium screen, individual conductors
C4 Copper braid screen
C5 Copper braid screen, individual conductors
C7 Copper tape screen
C8 Copper tape screen, individual conductors
D Screen of one or more thin steel tapes
- Armouring
Z2 Armouring of round steel wires
Z3 Armouring of flat steel wires
Z4 Armouring of steel tape
Z5 Braiding of steel wires
Z6 Supporting braid of steel wires
Z7 Armouring of sectional steel wires
Y2 Armouring of round aluminium wires
Y3 Armouring of flat aluminium wires
Y5 Armouring of special materials
Y6 Armouring of steel wires and/or tape and copper wires
Conductor Material
w/o designation Copper
- A Aluminium
- Z Special material and/or special shape
Special Design Features
- Supporting Structures
D2 Textile or steel wires over cable conductor
D3 Textile elements stranded in conductor cable
D4 Self-supporting cables and wires
D5 Central conductor element
- Special Versions
w/o designation round cable construction
H Flat type as separable cables with or without jacket
H2 Flat type of cables not separable
H3 Building Cable, flat webbed
H4 Multi conductor flat cable with one plain conductor
H5 Two or more single conductor stranded, non-jacket
H6 Flat cables with 3 or more conductors
H7 Cable with two-jacket extruded insulation
H8 Coiled conductor
Conductor Type
- D fine wire stranded for welding cables
- E extra fine wire stranded for welding
cables
- F fine wire stranded for flexible cables
- H extra fine wire stranded for flexible cables
- K fine wire stranded conductor for fixed installation
- M Milliken conductor
- R conductor of multi stranded wires
- S sector-shaped conductor of multi stranded wires
- U round conductor of single wire
- W sector-shaped conductor of single wire
- Y tinsel conductor
- Z conductor of special material
Protective Core
G with green/yellow earth conductor
X without earth conductor | Insulation & Sheath Materials
B Ethylene-propylene rubber (EDR) +90°C
B2 Ethylene-propylene rubber (EDR), hardened
B3 Butyl rubber
E Polyethylene
E2 Polyethylene, high density
E4 Poly-tetrafluorethylene
E5 Eethylene propylene rubber
E6 Ethylene tetrafluorethylene
E7 Polypropylene
G Ethylene-vinylacetate (EVA)
J Glass fibre braiding
J2 Glass fibre wrapping
M Mineral insulation
N Chloroprene rubber (CR)
N2 Chloroprene-rubber (CR), welding cable
N4 Chlorinated polyethylene
N5 Nitril-rubber
N6 Fluorinated rubber
N7 PVC nitril rubber compound
N8 Polychloroprene rubber, water resistant
P Impregnated paper insulation
Q Polyurethane (PUR)
Q2 Polyethyleneterephthalate
Q3 Polystyrole
Q4 Polyamide
Q5 Polyamide
Q6 Polyvinylidene fluoride
R (NR, SR) natural or synthetic rubber
S (SIR) silicone rubber
T Textile braiding
T2 Textile braiding with flame retardant
T3 Textile conductor wrapping or tape
T4 Textile conductor wrapping or tape, flame retardant
T5 Corrosion protection
T6 Textile braiding over individual conductor or cable
V PVC
V2 PVC soft, resistant to increased temperature, +90°C
V3 PVC soft, for low temperatures
V4 PVC soft, cross-linked
V5 PVC soft, oil resistant
X Cross-linked polyethylene
Z Cross-linked compound, LSZH
Z1 Thermoplastic compound, LSZH
Note: for details in insulation properties, please refer to:
- Cable Insulation Properties |
Cable Code Examples
Different manufacturers vary the way in which they present the harmonized designation for their cables. Here are a few examples of varying cable designations:
- H05VV5-F 2G075 is 00/500 V, PVC insulated, PVC sheathed, stranded flexible conductor, 2 core 2.5 mm2 with protective conductor
- H05V-K 1X1 is 300/500 V, PVC insulated, fine wire stranded, single core 1 mm2 with no protective conductor
- S03VV-F 3G0.75 is national standard (VDE in this case), 300/300 V, PVC insulated, PVC sheathed, fine wire stranded flexible cable, 3 core 0.75 mm2 with protective conductor
- H07RV-F 3X10 is 450/750 V, natural rubber insulation, PVC sheath, fine wire stranded, three core 10 mm2 with no protective conductor
- H05Z-K 1X2.5 is 300/500 V, XLPE LSZH, fine wire stranded, single core 2.5 mm2 without protective conductor
Cable Colour Codes
CENELEC (including BS 7671 - IEE Wiring Regulations)
| Function | Alpha-
numeric | Colour |
| Protective conductors | | Green and yellow |
| Functional earthing conductor | | Cream |
| a.c. power circuit |
| Phase of single-phase circuit | L | Brown 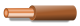 |
| Neutral of single- or three-phase circuit | N | Blue 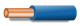 |
| Phase 1 of three-phase a.c. circuit
| L1 | Brown  |
| Phase 2 of three-phase a.c. circuit | L2 | Black  |
| Phase 3 of three-phase a.c. circuit | L3 | Grey 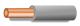 |
| Two-wire unearthed d.c. power circuit |
| Positive of two-wire circuit | L+ | Brown  |
| Negative of two-wire circuit | L- | Grey  |
| Two-wire earthed d.c. power circuit |
| Positive (of negative earthed) circuit | L+ | Brown  |
| Negative (of negative earthed) circuit | M | Blue  |
| Positive (of positive earthed) circuit | M | Blue  |
| Negative (of positive earthed) circuit | L- | Grey  |
| Three-wire d.c. power circuit |
| Outer positive of two-wire circuit derived from three-wire system | L+ | Brown  |
| Outer negative of two-wire circuit derived from three-wire system | L- | Grey  |
| Positive of three-wire circuit | L+ | Brown  |
| Mid-wire of three-wire circuit | M | Blue  |
| Negative of three-wire circuit | L- | Grey  |
| Control circuits, ELV and other applications |
| Phase conductor | L | Brown, Black, Red, Orange,
Yellow, Violet, Grey, White, Pink or Turquoise |
| Neutral or mid-wire | N or M | Blue |
If anyone notices any mistakes or corrections which are needed, please leave a comment below.