DC Motor Operation
Coils of wire on the rotor carry a d.c. current which generates a magnetic field. A stator magnetic field is created using either permanent magnets or electrical field windings.
Any current-carrying conductor placed within an external magnetic field experiences a force. Torque is produced in the motor by this mechanism.
As a d.c current provides a constant magnetic field, this needs to change each half revolution and is called commutation. Commutation is typically accomplished by metal brushes against the contacts. Where a field winding is used to generate the stator magnetic field, different motor characteristics can be obtained depending on how this winding is connected.
Operation Principals
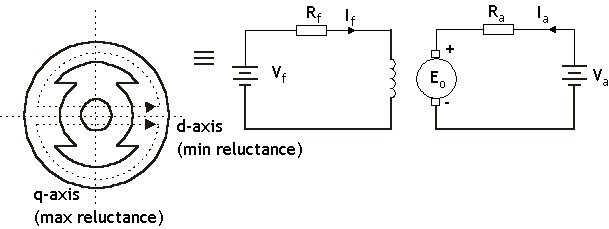 For the equivalent circuit the parameters are given by:
For the equivalent circuit the parameters are given by:
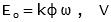 Where:
Where:
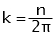 - lap winding
- lap winding
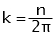 - wave winding
- wave winding
given that
- n = number of conductor
- p = number of pole pairs
- ω = motor speed, rad s-1
- φ = flux per pole, Wb
- T = torque Nm
and
The power input to armature is given by: 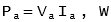
The armature power loss is given by: 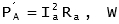
The output power is given by: 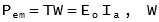
The torque is given by: 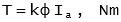
Typically, IaRa is ±3% of Va and the power dissipated in field winding ±3.5% of the motor rating.
Field Windings
Permanent magnets or field windings of a dc motor provide the necessary magnetic fields for the motor to operate(often call excitation):
- permanent magnets - provides a continuous and constant magnetic field by the use of permanently magnetized materials (typically on only the smallest motors)
- separately excited - separate windings and power supply provide the magnetic field for the motor
- shunt winding - this is connected in parallel with the motor armature to provide the excitation
- series winding - this is connected in series with the motor armature to provide the excitation
- compound winding - is a hybrid between shunt and series where to field windings are connected both in parallel and in series with the armature
Characteristics of DC Motors
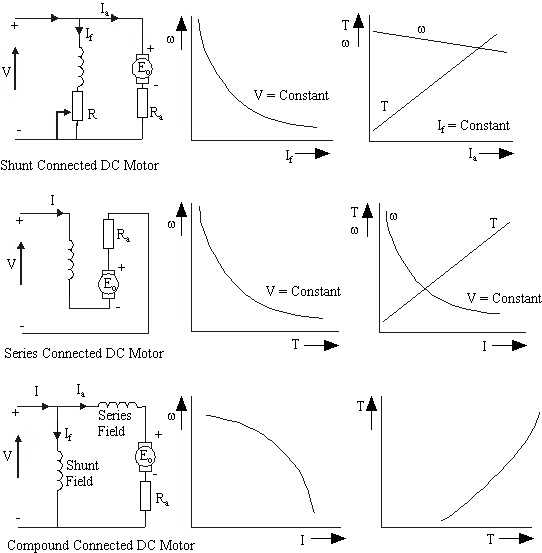
Speed Control of DC Motors
Separately excited, shunt
- Constant power drive - Ia,Va is held constant and If varied
- Constant torque If is held constant and Ia, Va varied
DC Converter output Voltages
Semi converter, 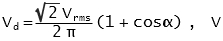 [DC converter equations do not look correct. Please can someone check.]
[DC converter equations do not look correct. Please can someone check.]
Full converter,
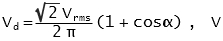
- with infinite inductive filtering