Differential protection, the good old days
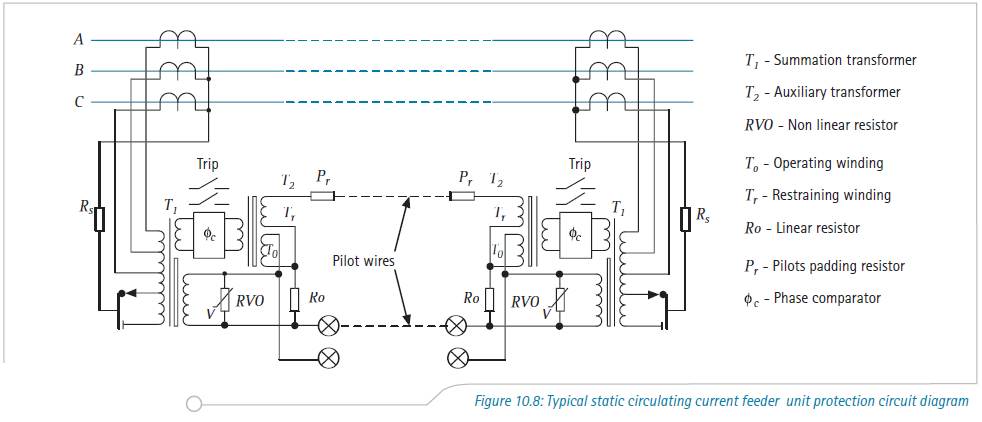
Image reproduced from
'Network Protection and Automation Guide, by Areva This morning I was explaining how differential protection works to a junior engineer. To give him something to read I opened up the NPAG (Network Protection and Automation Guide, by Areva) and turned to Chapter 10 ‘Unit Protection of Feeders’. I was immediately confronted with Marz and Price, circulating current systems, balanced voltage systems, high impedance series connected relays, illustrations like the one shown, etc. ... and remembered my early years. A time when if you mentioned differential protection to an electrical engineer, they would turn and run in the opposite direction.
Now, I’m not sure if this applies to everyone, but the systems I have been involved with for the past few years have employed numerical relays for differential protection. Install the two relays, connect together with an optical fibre and gone are all the problems of trying to do this using wires/current between the relays. I think this is a pretty clear example of how changes in technology have vastly simplified something. Not only has it simplified the application of differential protection, it also comes with a host of advancements – being able to use CTs manufactured to different specifications as an example.
Numerical relays and optical links may not be the answer to every situation, but I think they make life easier for most of us.