How to Size Power Cable Duct
 Some colleagues had an issue earlier in the week on sizing ducts to be cast in concrete for some power cables . It became clear that none of us had a clear idea on an approved method. In the end we agreed that selecting the duct based on a 40% fill factor was a good idea. This may not be the best approach. If anyone has other ideas, please add below.
Some colleagues had an issue earlier in the week on sizing ducts to be cast in concrete for some power cables . It became clear that none of us had a clear idea on an approved method. In the end we agreed that selecting the duct based on a 40% fill factor was a good idea. This may not be the best approach. If anyone has other ideas, please add below.
Using fill factor:
1. Required fill factor k (0.4 in our case)
2. Cable diameter Cd, giving cable area, a:
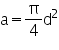
3. Cable total area Ca = sum of area for all cables
4. Minimum duct diameter Cc:
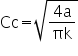
To make life a little easier, I have put together a cable duct sizing tool which will do the arithmetic.
Once the calculation is complete, choose the next largest size of ducts. What-if scenarios can also be carried out to optimize the quantity/size of ducts. In a real installation, it would be good practice to have multiple ducts the same size if possible and put a couple of spare ones in as well.
In addition to determining the size of cable ducts and number of cables, we also need to think about the maximum number of cables in a duct. The more cables, the more problems there will be with pulling (friction, bunching, etc.). It seems a good thing to limit the number of cables per duct to five or less.
This is a post that raises questions in addition to answers. If you have any good ideas or tips on the duct sizing, please add below. I'll add the good stuff into the post, so that over time we end up with a great resource.