Lead Acid Batteries
Lead acid batteries are cost effect and reliable, making them suitable for many applications.This note examines topics of interest associated with the use of these batteries.
Discharge & Peukert's Law
The capacity of lead acid batteries decrease as the charging rate is increased. The action of a battery under these conditions is described by Peukert's law (first proposed by German scientist Peukert in 1897):
Where:
t = time to discharge the battery, in S
Cp = battery capacity at 1 A.h discharge rate
I = the actual discharge current, in h
k = Peukert constant (dependant on battery, typically 1.1 to .13)
Typically batteries are rated at a discharge time, T (in hours) and rated capacity C. Perkert's law can then be expressed as:
Peukert's law is good for reasonably constant rates of discharge. For variable and non-linear rates, it starts to become inaccurate. Replacing I with the average current during the discharge will give a better result, but it is still limited. In this instance several methods can be used to improve accurately, including:
- Rakhmatov and Vrudhula Model - looks at the actual diffusion processes within the battery to derive a more accurate analysis
- Kinetic Battery Model - uses the chemical kinetics process as a basis for developing a discharge model
- Stochastic Models - analysis the battery as a stochastic process
Typical accuracy using Peukert's law is in the order of 10% error. Rakhmatov and Vrudhula models improve on this having errors around 5%, while Kinetic and Stochastic models perform even better with errors as low as 1 to 2%
[1].
Effect of Temperature
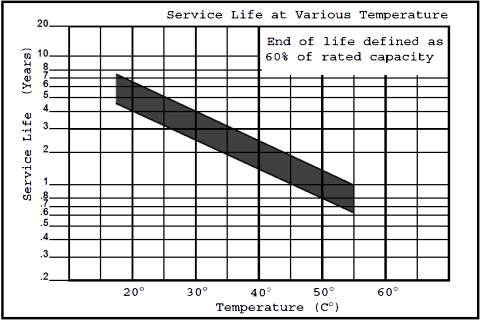 Effect of temperature on battery life
Effect of temperature on battery life
Lead acid batteries are cost effective and reliable, making them suitable for many applications. One serious drawback compared to some other batteries (NiCad for example), is that lead acid batteries are affected by temperature. Lead acid batteries should only be used where they are installed in conditioned environments not subject to excessive temperatures.
Typically the rating for lead acid batteries is based on an ambient temperature of 25oC. For every 8oC above ambient during use, the life of the battery will be reduced by 50%. Ideally batteries should be operated at 25oC or less.
In addition to operation, storage of batteries waiting for use is also affected by temperature. If lead acid batteries are stored at elevated temperatures (particularly in a discharged condition), they will effectively become useless. If storing batteries, they should be in charged and stored at 25oC or less. Batteries will self discharge over time and need to be recharged periodically.
References
- [1] Battery Modeling, M.R. Jongerden and B.R. Haverkort - doc.utwente.nl/64556/1/BatteryRep4.pdf, accessed November 2012.