Understanding electric motor insulation & temperature
 Anyone specifying or using electric motors should have a basic understanding how the insulation is related to temperature. Three classes of insulation are in common use (with 'F' being the most common):
Anyone specifying or using electric motors should have a basic understanding how the insulation is related to temperature. Three classes of insulation are in common use (with 'F' being the most common):
- class B - with a maximum operating temperature of 130 oC
- class F - with a maximum operating temperature of 155 oC
- class H - with a maximum operating temperature of 180 oC
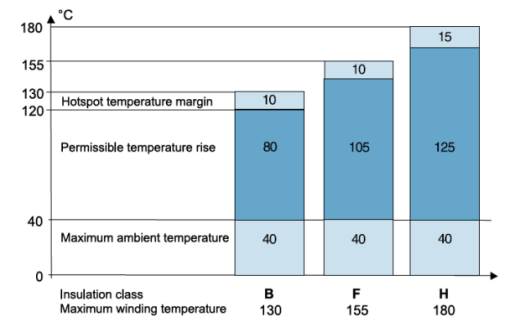
The image (which is form an ABB catalogue for their low voltage performance motors), shows how temperature rise is distributed across the insulation.
Typically motors are designed for a maximum ambient temperature of 40 oC.
The difference between the average winding temperature and any hot spot is limited and it is usual to allow a 10 oC margin for class 'B' and 'F' insulation and a 15 oC margin for class 'H'.
Considering the ambient temperature and hot spot allowance gives the maximum temperature rise within which the motor must be designed to operate (105 oC for class 'F' for example).
When specifying (buying) a motor there are a couple of options. An insulation class could be specified and the motor specified as designed to run within that class. Alternatively the motor could be specified for an insulation class, but be design to run at a low class (for example insulation class 'F', temperature rise 'B').
The advantage of the second method is that there is an inherent 25 oC safety margin - useful if you are in a region with high ambient temperatures or need to date the motor for some other reason. Running motors at a reduced temperature will also significantly extend the useful life.