Resistors

Resistors Resistors are electronic components that oppose the flow of current. Manufactured in various types and ranges they have a wide application to electronics.
The relationship between voltage and current in a resistor is given by Ohm's Law:
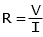
Identification and Values
Colour Code
When inspecting resistors, the given value is either printed on the body is can be determined from the resistor colour code.
Resistor Colour Code
Example
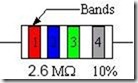
Red(2)Blue(6)Green(5)
=2600000
=2.6 MΩ
The first two bands are the value and the third band is a decimal multiplier (10x).
| Black |
Brown |
Red |
Orange |
Yellow |
Green |
Blue |
Violet |
Grey |
White |
|
0
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
9
|
The fourth band give the tolerance:
| Gold |
Silver |
None |
|
5%
|
10%
|
20%
|
For precision resistors, sometimes a five band colour coding is used – first three bands are the value, fourth band is the multiplier and the fifth band is the tolerance.
Preferred Values
Resistors are manufactured and specified in a range of preferred values.
The table shows the range of preferred values:
| 10 |
12 |
15 |
18 |
22 |
27 |
33 |
39 |
47 |
56 |
68 |
82 |
Note: to obtain full range, multiply table by 10X
Circuit Arrangements
For more information on circuit arrangements and how to work these out, please see the following note: