Motor Starting - Introduction
 Electric motor driving a pump
Electric motor driving a pump Motor starting and its associated problems are well-known to many people who have worked on large industrial processes. This post is a quick introduction to motor starting.
Motors have been in use for over 100 years, and during that time there has been relatively little change in how they function. The induction motor is by far the most widely used motor in industrial and building applications. As such, this book concentrates primarily on the application of motor starting in connection with induction motors.
Induction motors rely on the interaction of magnetic fields to convert electrical power into rotating power. The build-up of magnetic fields and back electro-motive force, or back emf, during the motor starting time introduces transient conditions into the electrical system. These transient events can affect the electrical supply system and other equipment connected to it. The key reasons consideration is given to motor starting are: to limit the transient effects; and to ensure that the motor accelerates the mechanical load correctly
Motor starting time, starting current, and starting transients
Motor starting time is the period from when the electrical supply is connected to the motor to when the motor accelerates to full speed. The length of the starting period is dependent on the combination of the motor and mechanical load, and it can be anything from a fraction of a second to 30 seconds or longer.
High levels of current are required during the start-up period, and they can have detrimental effects on the electrical supply system and other equipment connected to it. The duration of starting transients depends on the load characteristics and how long it takes the motor to run up to speed.
The figure below illustrates what happens during motor starting. During the starting period a current significantly larger than the motor’s normal full load running current is drawn, the magnetic fields within the motor and back emf increase, and the mechanical load accelerates. The start-up current can be as high as five to eight times the full load current.
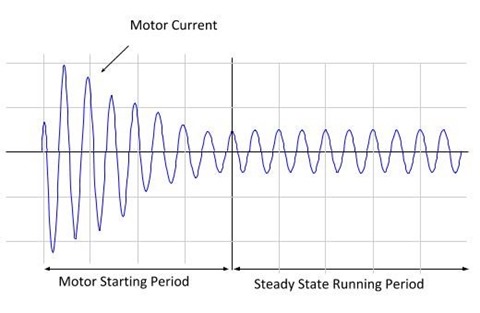 Motor current during starting and running
Motor current during starting and running Electrical systems are designed to cater for the steady state running period conditions. The cables are sized to accommodate the steady state running conditions, and voltage drops across the electrical system are calculated based on the steady state conditions.
During the motor starting period the cables will carry more current than during the steady state running period. System voltage drops will also be much larger during the starting period than during the steady state running period – this becomes particularly apparent when large motors are started, and / or if many motors are started at the same time.
If the voltage drop to the motor itself is too great during the starting period, the motor may be unable to develop sufficient torque to accelerate the mechanical load. In addition, voltage drops within an electrical system may affect other equipment, even to the extent of causing failures.
As the use of motors became widespread, overcoming motor starting problems became a concern for engineers. Over the years, many methods and techniques – each with its own advantages and limitations – have been developed to address the issues around motor starting.
The more commonly used methods of motor starting are:
- Direct On Line
- Star Delta
- Auto-Transformer
- Primary Resistance
- Rotor Resistance
- Electronic Soft Start
DOL and star-delta are by far the most commonly employed methods of motor starting. However, there have recently been massive strides made in the utilisation of electronics in regulating electrical power to motors, and electronic starting is fast catching up with DOL and star-delta. These advances can be utilised to allow the motor to operate with very specific acceleration characteristics.
This introduction to motor starting is an extract from my short introductory book on the subject. If you want to delve into motor starting and understand how to the various types of starter work, please check out book.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Motor Starting
Direct On Line Starting
Star-delta Starting
Auto-transformer Starting
Primary Resistance Starting
Rotor Resistance Starting
Electronic Soft Start
Variable Frequency Drives
Summary of Motor Starting Methods
How To Calculate Motor Starting Time
Useful Motor Technical Information
Typical Motor Starting Design Information
List of Symbols & Glossary

The book is available in paperback eBook format at all Amazon stores.