How to refer fault levels across a transformer
Over the past year or so I have been involved in on going discussions related to referring fault levels from the secondary of a transformer to the primary side. While this is easy for some people to grasp, for others it's not so straight forward. Here is a brief explanation of how to do this.
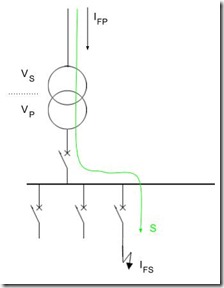 The image shows a simple electrical system around a transformer (primary voltage VP, secondary VS). A fault, IFS (shown on the secondary), will also been seen on the primary side of the transformer IFP. Because, the voltage level on the primary of the transformer is different than the secondary, the two values of current will be different.
The image shows a simple electrical system around a transformer (primary voltage VP, secondary VS). A fault, IFS (shown on the secondary), will also been seen on the primary side of the transformer IFP. Because, the voltage level on the primary of the transformer is different than the secondary, the two values of current will be different.
The value of the primary side fault current is determined by the ratio of the transformer voltages:
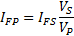
That really all there is to it. If you wanted to refer from the primary to the secondary, just reverse the ratio of the voltages.
Proof of correctness
To verify that the above is true, consider the power (S) transfer from the primary to the secondary of the transformer; shown by the green line. The power is the flow of energy into the fault and the 'law of conservation of energy' states that the energy entering the system must be the same as that exiting the system.
Ignoring losses (which are small compared to the fault), the power (energy) into the fault must be supplied by via the primary of the transformer and is the same on both sides of the transformer.
In a single phase system, the electrical power is given by:
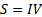
applying to both the primary and secondary circuits:
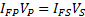
which can be rearranged to give:
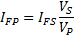
For a three phase system (with a symmetrical three phase fault), we have the same result. The power would be three times that of a single phase system, with voltages as line to neutral. The three on both sides of the equation cancel, leaving the same answer.
For three phase systems, unbalanced or earth faults are more problematic. In these instance it is better to use techniques such as symmetrical components to calculate what is happening.
If you need a little more information on working three phase power from single phase power, you can see:
Any other tips or insights, please add to the comments below.