DC Component of Asymmetrical Faults
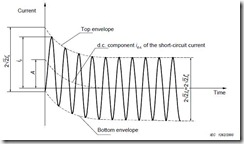 The image (reproduced from IEC 60909) shows a typical fault in an ac system. From the illustration it can seen that there is an initial dc component (id.c.). This initial dc component decays over time, eventually reaching zero. Addition of the dc component to the symmetrical short circuit current gives the asymmetrical fault current.
The image (reproduced from IEC 60909) shows a typical fault in an ac system. From the illustration it can seen that there is an initial dc component (id.c.). This initial dc component decays over time, eventually reaching zero. Addition of the dc component to the symmetrical short circuit current gives the asymmetrical fault current.
The initial value of the dc component is dependant on the exact time within a cycle at which the fault takes place and the value of current at that time.
At the initiation of a fault, the current in any system inductance cannot instantly change from it’s value at fault inception to that of it’s steady state fault value. To compensate for this, a dc component is introduced. The dc component is equal to the value of the instantaneous ac current at fault inception and of opposite polarity.
Magnitude of the dc component is dependant on where in the cycle the fault inception takes place. In the worse case, the initial dc offset will be √2 times the symmetrical short circuit value (RMS).
The dc component decays exponentially according to:
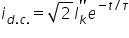
Where:
Ik’’ = symmetrical short circuit current (RMS) (kA)
τ = decay time constant (s)
t = time since fault inception (s)
The time constant τ, is dependant on the system reactance, X and resistance, R and at frequency f is given by:
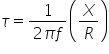
Application to Circuit Breakers
Application of the above knowledge to circuit breakers is worth mentioning (we have had a question asked on this recently).
For most distribution circuit breakers, a system time constant of dc decay of 45 ms (X/R of 17 at 60Hz) is assumed. Using this assumption, in a distribution application, the dc component is nearly completely decayed after just a few cycles.
Where the system X/R ratio is greater, it will result in a larger time constant, slower decay of the dc component and additional stress on the circuit breaker. In these instances the circuit breaker needs to be selected accordingly.
As an example, generator circuits typically have a higher X/R ratio and circuit breakers manufactured for this type off application would typically be designed for a system time constant of 133 ms (X/R ratio of 50 at 60 Hz).
The above is a brief introduction to the dc component of asymmetrical fault currents. If you want to delve into more detail, the IEC 60909 standard “Short-circuit currents in three-phase a.c. systems” is a good starting point.
If you have any immediate questions or comments, please post below.