Why a Sine Wave?
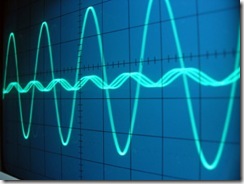
Sine Waves on an Oscilloscope I received this question by email a few weeks. First thoughts was that it is a product of the mathematics of rotating a straight conductor in a magnetic field. While I guess this is the primary issue, after some thinking I have come up with few reasons why a sinusoidal wave is advantageous:
Physics of rotating machines
To generate electricity it is necessary to continually move a conductor through a magnetic field. A practical and easy method is to continually rotate the conductors in a magnetic field. The physics of doing this naturally result in the production of a sinusoidal waveform (see note on sine wave generation for more details).
Historical Reasons
Early generation was easy to implement using rotating machines. Today it would be relatively easy to generate a variety of waveforms (using Pulse Width Modulation for example). With the extensive existing sinusoidal based infrastructure, it is unlikely that other types of wave form will be adopted. There may potentially be certain applications where the use of a different type of waveform may be beneficial.
Voltage Transformation
The problem of transformation of voltages for long distance transmission is conveniently solved by the use of sinusoidal waves. A the current is continually varying, so is the magnetic field it produces enabling the development of transformers. With modern advances in power electronics, there are alternatives now available which are being employed (for example in the transmission of dc power).
Technical Considerations
Electrical systems primarily consist of resistance, inductance and capacitance. The relationship between voltage and current for each case is:
- Resistance
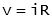
- Inductance
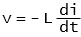
- Capacitance
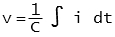
Integrating or differentiating a sine function results in a cosine (or shifted sine) function. System design around this becomes relatively easy. Compare this with say a square wave, where di/dt at the direction change there would be very large non-linear voltages created.
Related Links