Back to basics - the Watt (or kW)
When thinking about watts (W) or kilowatt (kW = 1000 W) it can be useful too keep in mind the fundamental ideas behind the unit. Watt is not a pure electrical or mechanical unit, but is a measure of the rate of doing work.
Let start at the beginning and understand the meaning of work. This is effectively what the word says; doing work involves doing something - like moving things from one place to the other, climbing stairs, etc. In physics this is equated to the energy used in in transferring a force through a distance in the direction of the force. The SI unit of work is the Joule.
Another more general way to look at work it to consider that if the force acting on an object changes it's kinetic energy then the work done is equal to the change in kinetic energy.
So does work = force x distance? Sometimes. Work is a scalar quantity and this equation holds if the force is acting in the same direction as the movement. If the force and distance are not acting in the same direction then we need to take the dot product of the force and distance vectors:
|

James Watt
19 January 1736 - 19 August 1819 |
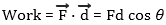
If the angle θ is zero the work is simply the force multiplied by distance If the force is perpendicular to the distance, cos θ = 0 and no work is done.
With an understanding of work, we can get back to the main topic - Watts. This is simply a measure of the rate at which work is carried out, i.e.:
1 Watt = 1 Joule of work per Second
What is the rate of doing work? The answer is Power. If we want to measure the power of a car or electrical motor we want to look at the amount of energy it can deliver every second (i.e. Watts). The unit Watt is named after the Scottish engineer James Watt (famous for his work on steam engines).
With an understanding of the concepts, an example will tie everything together:
Example: a 50 kG weight is lifted vertically 20 m in 10 seconds (with the lifting force acting in the same direction as the movement):
Work done = 50 x 20 = 1,000 Joules
The work is done over 10 seconds, so the average power (rate of using energy) is:
Power = 1,000 / 10 = 100 Watts
That’s it. Before finishing a few final observations:
-
1 kW (kilowatt) is 1000 W (Watts). Watt is the SI unit or power, although in the United States horse power (HP) as a unit is still common. One HP is nominally the amount of energy a horse could deliver each second. As each real horse is different this has been standardised to the Watt, with 1 HP = 764 Watts
-
kWHr (kilowatt-hours) is the power multiplied by the time it is used. For example if 1 kW is used for 2 hours than 2 kWHr is used (or 2,000 W x 7,200 seconds = 14.4 10^6 Watt-Seconds). Form the above, 1 watt-second is 1 Joule (i..e the energy expended). kWHr measures energy and not power